Molecular biology
The study of the genetic and molecular mechanisms that underlie the unique survival abilities of tardigrades.
Introduction
Tardigrades, often referred to as “water bears,” are tiny, water-dwelling creatures that have captivated scientists with their extraordinary survival capabilities. These remarkable organisms can withstand extreme conditions, including desiccation,high radiation levels, and extreme temperatures. The field of molecular biology delves into the genetic and molecular mechanisms that underlie these unique survival abilities of tardigrades. By understanding the molecular processes involved, scientists aim to unlock the secrets of tardigrade resilience and potentially apply these findings to various scientific and practical applications
1.The Importance of Molecular Biology in Tardigrade Research
Molecular biology plays a crucial role in unraveling the mechanisms that enable tardigrades to survive in harsh environments. By studying the genetic makeup and molecular processes of tardigrades,researchers gain insights into the specific adaptations and protective strategies these organisms employ.
2. DNA Repair Mechanisms in Tardigrades
Tardigrades possess exceptional DNA repair mechanisms that contribute to their survival in extreme conditions. These mechanisms involve various proteins and enzymes that repair DNA damage caused by radiation, desiccation,and other stressors. Understanding the intricacies of tardigrade DNA repair systems may provide valuable insights into human health, as these mechanisms could potentially be harnessed for medical applications.
3. Protein Stabilization in Desiccated Tardigrades
One of the most fascinating aspects of tardigrade biology is their ability to enter a desiccated state, where they lose almost all of their body water content. During desiccation,tardigrades employ unique molecular strategies to stabilize their proteins and prevent irreversible damage. By studying these mechanisms, scientists hope to gain insights into protein stability and develop novel methods for preserving proteins under extreme conditions.
4. Genomic Analysis of Tardigrades
Genomic analysis is a powerful tool used in molecular biology to uncover the genetic basis of unique traits & adaptations. In the case of tardigrades, scientists have sequenced their genomes to identify genes that contribute to their survival abilities. These genomic studies provide a foundation for further investigations into the molecular mechanisms underlying tardigrade resilience.
9. Anhydrobiosis: The Key to Tardigrade Survival
Anhydrobiosis is the ability of tardigrades to enter a state of suspended animation in response to desiccation. Molecular biology investigations into the genetic and molecular mechanisms of anhydrobiosis shed light on the intricate pathways that enable tardigrades to survive in a dehydrated state. This research holds promise for developing new strategies for preserving biological materials and advancing fields such as cryobiology.
5. Stress-Response Pathways in Tardigrades
Tardigrades activate specific stress-response pathways in response to adverse conditions. These pathways involve the expression and regulation of various genes and proteins that protect the tardigrades’ cellular structures. Molecular biology studies shed light on the intricacies of these pathways,helping scientists understand the molecular switches that allow tardigrades to adapt and survive under extreme stress.
6. Trehalose: The Protective Sugar Molecule
Trehalose, a unique sugar molecule, is found abundantly in tardigrades and is associated with their desiccation tolerance. Molecular biology investigations have revealed that trehalose acts as a protectant, stabilizing proteins and cellular structures during desiccation. Unraveling the molecular mechanisms of trehalose’s protective properties may pave the way for the development of novel preservation methods and biotechnological applications.
7. The Role of Heat Shock Proteins
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are essential components of cellular stress response systems. Tardigrades possess a diverse array of HSPs that are activated during adverse conditions. These proteins play a crucial role in preventing protein misfolding, aggregation, & cellular damage. Understanding the molecular functions of tardigrade HSPs may contribute to advancements in stress tolerance research and therapeutic strategies.
8. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Tardigrades
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) refers to the transfer of genetic material between different species. Tardigrades exhibit a surprising degree of HGT, which has implications for their survival abilities. Molecular biology studies have revealed instances of tardigrades acquiring genes from bacteria, fungi, and other organisms. Investigating the mechanisms and functional implications of HGT in tardigrades broadens our understanding of the evolutionary processes and the potential transfer of unique genetic traits.
FAQ's
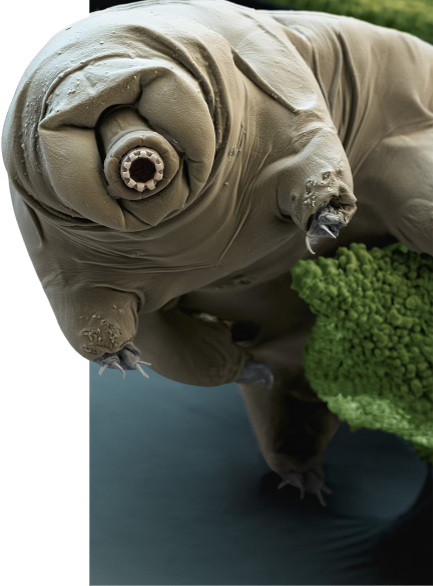
Ans. Studies have shown that tardigrades can withstand the vacuum and radiation of outer space. In laboratory experiments, tardigrades exposed to the harsh conditions of space have been able to survive and reproduce upon returning to Earth.
Ans. Tardigrades possess unique DNA repair mechanisms that can efficiently repair DNA damage caused by high levels of radiation. Additionally, tardigrades’ ability to enter a desiccated state further protects them from radiation’s harmful effects.
Ans. Yes, tardigrades are incredibly resilient and can be found in various environments worldwide, including freshwater, marine habitats,&even the most extreme environments like Antarctica and the deep sea.
Ans. Studies have shown that tardigrades can withstand the vacuum and radiation of outer space. In laboratory experiments, tardigrades exposed to the harsh conditions of space have been able to survive and reproduce upon returning to Earth.
Ans. When tardigrades are rehydrated after desiccation, they gradually resume metabolic activity, repair cellular damage,& return to their active state. The precise molecular mechanisms involved in this recovery process are still being investigated.
Ans. The unique molecular mechanisms and stress response pathways found in tardigrades hold potential for various medical applications. Researchers are exploring tardigrade proteins and compounds for their use in protecting human cells and tissues from stress and damage.
Ans. Contrary to popular belief, tardigrades are not immortal. While they can withstand extreme conditions & enter a dormant state, tardigrades still have a finite lifespan and eventually die.
CONCLUSION
Molecular biology is the key to unraveling the genetic and molecular mechanisms that allow tardigrades to survive and thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth. By studying these fascinating organisms at the molecular level, scientists are gaining valuable insights into stress tolerance, DNA repair, protein stability, & other biological processes. The discoveries made in tardigrade research have the potential to revolutionize various fields, from medicine and biotechnology to space exploration and conservation efforts. The study of molecular biology in tardigrades highlights the incredible adaptability and resilience of life forms and showcases the intricate web of biological processes that enable survival against the odds.
